Abdominal Pregnancy – Symptoms, Risks, and Treatment
Abdominal pregnancy is rare but can pose certain health risks when it occurs. Abdominal pregnancy is a form of an ectopic pregnancy (where the embryo is not attached to the uterus). The symptoms of an abdominal pregnancy and normal uterine pregnancy do not vary a lot, but it is important to identify the details so that it can be diagnosed.
What Is Abdominal Pregnancy?
An abdominal pregnancy occurs when a fertilised egg implants itself on the tissues or an organ in the abdomen of the woman. This condition is extremely rare but can possess many health risks if occurs.
Primary Abdominal Pregnancy
Primary attachment of the embryo is when the embryo is attached and implanted directly in the abdomen. The chance of this happening is extremely rare.
Secondary Abdominal Pregnancy
Secondary abdominal pregnancy is when the foetus starts to grow in the ovaries or the fallopian tube, but because of a small rupture, the embryo gets implanted in the abdominal cavity. In abdominal cavity pregnancy, the pain that is experienced by the woman is similar to the pain experienced during tubal pregnancy. If the foetus continues to grow, abdominal pains start after 26–28 weeks into the pregnancy.
The fallopian tube may rupture in the first trimester of the pregnancy. The skin becomes pale because of the resultant bleeding that is accumulated in the abdominal cavity.
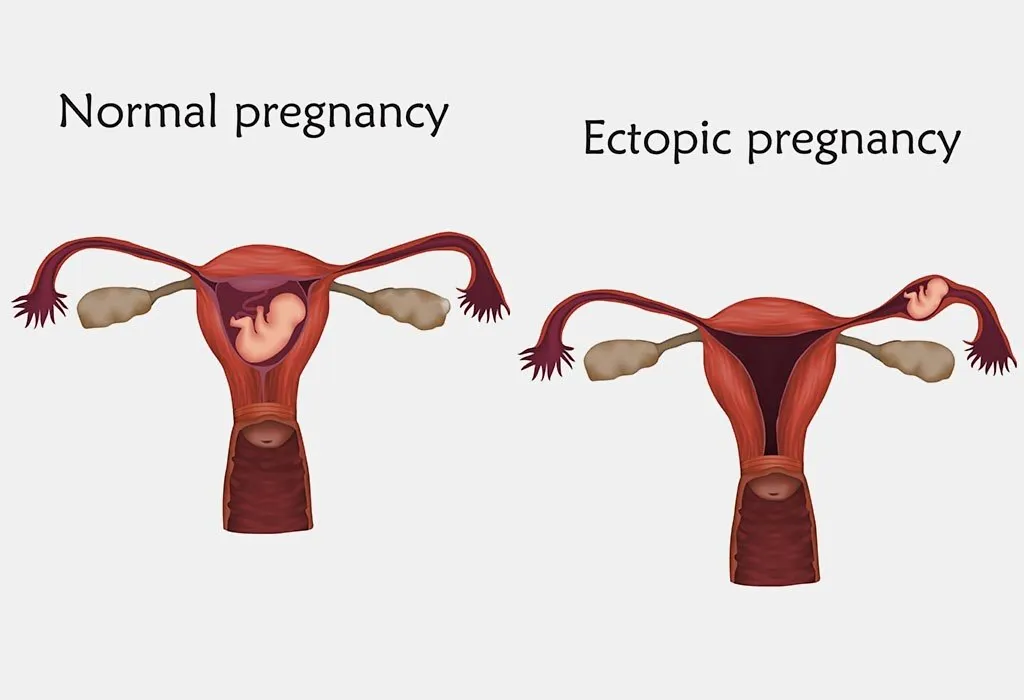
What Are the Symptoms of Abdominal Pregnancy?
A woman who has abdominal pregnancy will have the same symptoms and signs that pregnant women experience in general.
- Breast tenderness
- Nausea and vomiting (occasionally)
- Fatigue
- Abdominal pain and vaginal bleeding
Vaginal bleeding and abdominal pain should be checked out by a doctor as this is not normal.
How Is Abdominal Pregnancy Diagnosed?
Until the late stage, many abdominal pregnancies are left undiagnosed. A doctor might suspect it to be an abdominal pregnancy when the woman reports pain when the foetus moves, or if the growing foetus is not at the right place in a woman’s body.
This condition can also be indicated by the blood tests that measure human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) levels if the levels of the hormone are not rising normally as it should be when the pregnancy progresses.
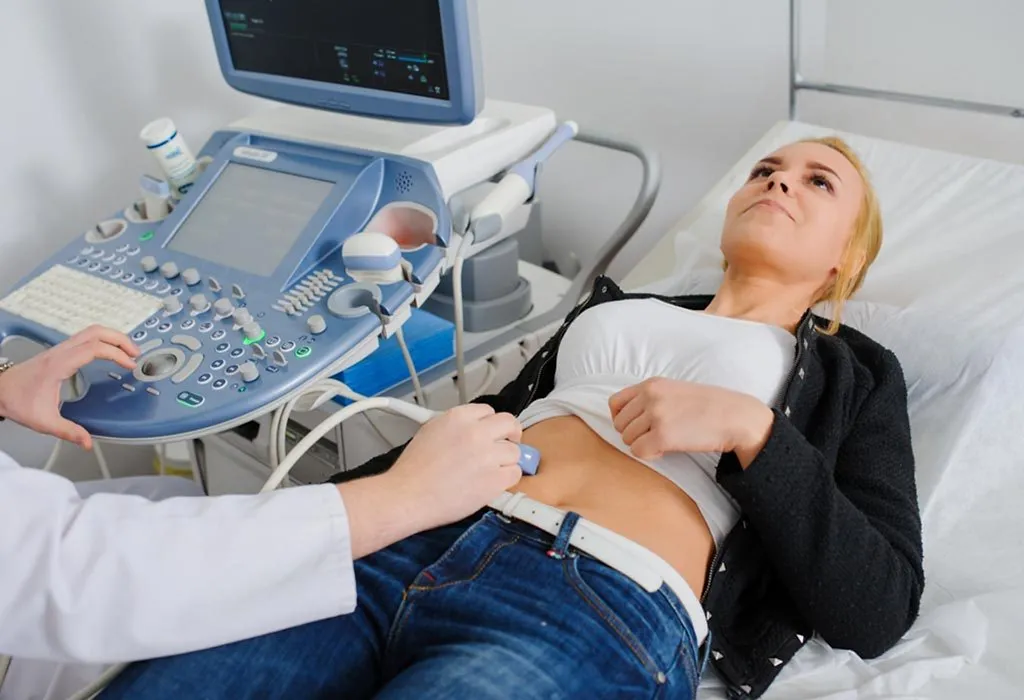
Usually, an abdominal pregnancy is diagnosed through an ultrasound. To create images of the internal structures, ultrasound uses sound waves. The location of the gestational sac is confirmed using ultrasound. Some cases also include the use of laparoscopy to confirm the diagnosis, which is the insertion of a very tiny instrument into the abdomen.
What Are the Risks of Abdominal Pregnancy?
An ectopic pregnancy can be dangerous for the mother and the child. Following things may happen in case of abdominal pregnancy:
1. Heavy Internal Bleeding
If the placenta detaches from the tissue or abdominal organ to which it was attached to, then the pregnant woman may experience heavy internal bleeding. This could lead to a serious outcome if the mother does not receive timely diagnosis and treatment.
2. Inadequate Supply of Nutrients
In the case of abdominal pregnancy, the foetus may not receive enough nutrients and blood for his proper growth. The foetus may also not be protected by the amniotic sac and fluid which it usually is when growing in the uterus.
3. Increased Foetal Movement
In the case of abdominal pregnancy, the foetal movements are likely to be more than normal and also very painful. Moreover, in the normal areas of the body, the foetal movements would not be felt. The reason for this is the foetus lying sideways across the abdomen. It might also be in the oblique position in the abdomen.
4. Depression
If there is pregnancy loss, the woman might end up grieving over the loss of the foetus and might start worrying about future pregnancies.
Treatment for Abdominal Pregnancy
There are some rare cases where abdominal pregnancy has resulted in live births. However, most abdominal pregnancies are terminated surgically or medically. If the doctor figures out a case of abdominal pregnancy early, a dose of methotrexate will be given to end the abdominal pregnancy. This is a drug that stops the cells from dividing, and it is toxic to the placenta. When the abdominal pregnancy is ended through surgery, the surgeon will have to take certain steps to prevent heavy bleeding at the place of the implantation. In many cases, the placenta is left in the mother’s body, and it is treated with methotrexate, as it prevents heavy bleeding and may allow the body to reabsorb the placenta.
The causes of abdominal pregnancy cannot be prevented. Other serious complications might also occur because of abdominal pregnancy like intestinal obstruction symptoms which might also cause a high fever. It is important that this form of pregnancy is detected as soon as possible.
Also Read:
Heterotopic Pregnancy: Symptoms and Treatment
What is a Chemical Pregnancy?
Overdue Pregnancy: Causes & Tips to Survive