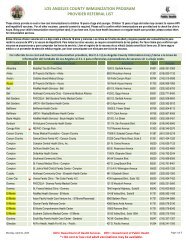
Fibrocystic Breasts
Fibrocystic Breasts
Fibrocystic Breasts
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
<strong>Fibrocystic</strong> <strong>Breasts</strong><br />
<strong>Fibrocystic</strong> changes are the most common cause of breast lumps in women from 30 to 50 years of age.<br />
<strong>Fibrocystic</strong> changes may also be called fibrocystic disease, cystic disease, or chronic cystic mastitis.<br />
<strong>Fibrocystic</strong> changes are not cancer.<br />
Diagnosing <strong>Fibrocystic</strong> Changes<br />
<strong>Fibrocystic</strong> changes may be found by physical examination, mammography or ultrasound. <strong>Fibrocystic</strong><br />
changes may also be diagnosed with a breast biopsy. Very few women who have a breast biopsy for a<br />
fibrocystic condition have the type of change that would be considered a risk factor for breast cancer.<br />
Cause of <strong>Fibrocystic</strong> Changes<br />
<strong>Fibrocystic</strong> changes are related to the way breast tissue responds to the female hormones, estrogen and<br />
progesterone.<br />
<strong>Fibrocystic</strong> Changes<br />
<strong>Fibrocystic</strong> changes are most often found in both breasts and commonly found in the upper outer part of<br />
the breast and the underside of the breast. When the breast tissue is stimulated by the hormones<br />
during the menstrual cycle, swelling occurs in the blood vessels of the breast. The milk glands and milk<br />
ducts become larger and the breasts retain fluid. The breasts may feel swollen, tender and lumpy. Som<br />
women may have tenderness while others may have severe pain. Each month after a woman has her<br />
r period, the swelling in the breast decreases and the breasts feel less tender and lumpy.<br />
After repeated stimulation by the hormones, the breast may have an increase in firmness. Pockets of fluid<br />
called “cysts” may form in the milk ducts. After menopause, the breasts may be less sensitive. However,<br />
fibrocystic changes may continue for women who choose hormone replacement.<br />
Cysts<br />
Cysts are fluid filled pockets in the breast. Large cysts usually feel firm, smooth, moveable and tender.<br />
Smaller cysts may feel like tiny beads in the breast. The tenderness and the size of the cysts usually<br />
increase the week before the menstrual period and decrease the week after the menstrual period. Simple<br />
cysts can be drained with a syringe and needle in a doctor’s office. Surgical removal (biopsy) is usually<br />
not necessary.<br />
Lumps versus <strong>Fibrocystic</strong> Changes<br />
Not all women who have breast lumps have fibrocystic changes. The normal structures of the breasts,<br />
the milk glands, the ducts and the fibrous tissue make the breasts feel lumpy. By doing Breast Self<br />
Examination (BSE) each month, a woman will learn what is normal for her. When she feels a change,<br />
(Cont. on Back)<br />
Accredited by Accreditation<br />
Association for Ambulatory Health Care, Inc.
she will know to consult her health care provider who may recommend a mammogram or an ultrasound of the<br />
breast.<br />
Treatment of <strong>Fibrocystic</strong> Condition<br />
Women who have painful breasts may find some relief with local heat application and a good support bra.<br />
Avoiding food and drink that contain caffeine may relieve symptoms. A health care provider may recommend<br />
aspirin or other pain relievers. Some lumps may need to be removed surgically. This is the type of lump that<br />
fails to disappear after observation and attempts by a doctor to remove fluid.<br />
(Source: American Cancer Society [http://www.cancer.org] & printed with their permission)<br />
Rev. 07/09