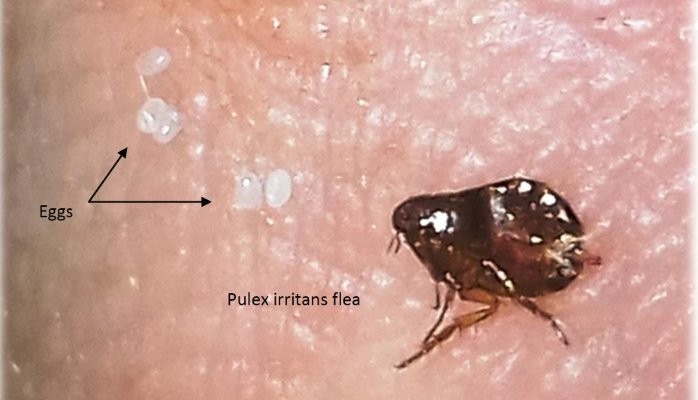
Pulex irritans on human skin
The species Pulex irritans, known as human flea, has a wide host spectrum (generally mammals) in tropical regions, but it is less-commonly seen in industrialized areas. It seeks a worm-blooded host for blood meals. In terms of sexual dimorphism, females are larger than males. Eggs may be either laid in the host's place of rest, often called environmental hot spots, or directly on the host.
The 0.5 mm eggs are oval shaped and pearly white in color (black arrows). They are often laid on the body of the host, but since they are not sticky or cemented down, they can fall off in many different places.
Pulex irritans will attach to and begin feeding on the skin. They are a pest species, causing an itching sensation that results in discomfort and leads to scratching in the vicinity of the bite. Flea bites generally cause the skin to raise, swell, and itch. The bite site has a single puncture point in the center. Bites often appear in clusters or small rows and can remain inflamed for up to several weeks