Breast Diseases - Diagnosis and Treatment
Breast Pain (Mastodynia or Mastalgia):
Breast pain is usually caused by a Benign Condition like inflammation, especially during lactation. Breast pain also occurs in the premenstrual period due to congestion. It might also occur in excessive intake of caffeine products like coffee, tea, cola and chocolates. Sometimes breast pain occurs in association with some medications. If breast pain is localized, we should look for an underlying lesion. Breast pain in both breasts does not worry us and usually occurs in the premenstrual period. We then advise the patient to cut down on salt intake during this period. Treatment of breast pain includes NSAIDs like Brofen and Evening Primrose Oil (EPO) tablets.
Breast Inflammation:
Breast inflammation is manifested by pain, skin redness, and localized swellings of the inflamed area. Usually, it occurs during breastfeeding and rarely in unmarried women. If untreated, it might progress into an abscess. Most often breast inflammation is successfully treated with antibiotics and anti-inflammatory agents like Brofen.
If an abscess occurs, this should be treated without delay with incision and drainage under general anesthesia.
Breast Abscess:
Breast Abscess is usually manifested by painful and congested swelling near the nipple. Affected area usually feels warm or hot. It may or may not be accompanied by generalized fever. Many times the inflamed area can regress on antibiotics before it develops into an abscess. However, when the affected area feels soft (fluctuant) and quite tender it needs surgical incision and drainage. Immediately the pain and fever disappear and the patient feels better.
Nipple oozing:
Nipple oozing can be a clear liquid, milky discharge, or bloody discharge. It may have different colors ranging from yellow to greenish to brownish. All colors indicate that the lesion is benign. Only the bloody discharge and serious discharge are significant because they might be caused by duct papilloma or cancer. Frequently the site of the papilloma can be defined clinically by pressing on the skin around the nipple. When we reach over the papilloma then there will be secretion on pressure. Thus we know at what axis the lesion is. This will help us to identify the region of pathology and excise it. However, in most cases, the treatment is best done by total duct excision.
Mammogram and Ultrasound:
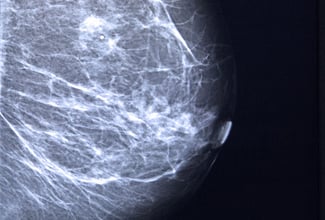

For screening purposes, Mammogram is advised to be done once a year for all women after the age of 40 and we call it screening mammogram. Mammogram when done for a woman with breast mass, we call it a diagnostic mammogram and this can help us in identifying breast cancer in 90% of cases as it shows irregular dense mass or mass with many microcalcifications. The ultrasound is helpful in distinguishing breast mass from being cystic or being solid. The solid mass on ultrasound can be cancer if it is non-homogenous, hypoechoeic, and if the perpendicular length is larger than the horizontal length of the lesion.
Both mammogram and ultrasound should be done routinely for diagnostic purposes. We are often asked by patients about the harm of X-rays caused by mammograms. Actually, the amount of x-ray by the mammogram is less than that of chest film or dental x-ray for teeth.
Breast Cysts:
The Breast cysts are usually manifested as a tender moveable mass. It is usually firm and can be diagnosed as cysts and not cancer on ultrasound. It is usually treated by aspiration in the office. If the aspirated fluid is bloody or the cyst does not disappear completely on aspiration, then surgery is advised. If the aspirated fluid is not bloody or not serous (clear yellow), there is no need to send it for cytology because it is always benign.
Fibro Adenoma:
This is the most common lesion in girls and women between the ages of 15 to 30. It can be solitary or multiple and it can occur in both breasts. Usually, they are painless and mobile lesions. They grow in size very slowly. They feel firm and might be lobulated. On exam, they move and that’s why they are often called breast mice.
On ultrasound, they appear homogeneous and hyperechoic. Their maximal length is longitudinal. Treatment of fibro adenoma is excision as I prefer. Some prefer to observe them and only remove them if they grow fast. However, this creates anxiety for the patient. In the end, the lesions are removed. That’s why I personally prefer to remove them from the beginning. In rare cases, the fibro adenoma is found big from the start and called the giant fibro adenoma. This might transform into something called cystosarcoma phylloides. This lesion is usually benign but in some cases, it could be malignant.
Fibro Cystic Disease:
This is also called Fibrous Mastopathy or fibrocystic changes. This lesion is quite common. It occurs usually between the ages of 30 to 50. It is made of thick breast tissue that contains within it cystic areas and fibrous tissue. It is manifested by thickened and lumpy breast areas that are usually painful. It is usually benign but in rare cases, it might be associated with cancer. Thus it is advised to do a Biopsy on these cases to rule out cancer or excise the lesion as a whole and send it to pathology.
B



.jpg?width=1000&name=1080%20(13).jpg)





.jpg?width=1080&height=1080&name=DR%20HASSAN%20ALSHATER%20(1).jpg)

