Cystic Fibrosis: Causes, Inheritance, Treatment and Diagnosis
What is Cystic Fibrosis?
Cystic fibrosis (CF) is a genetic disorder that impairs the body's ability to produce sweat and thick mucus. CF causes mucus to build up in the lungs. This mucus clogc the lungs, preventing them from functioning properly. CF can lead to infection, breathing problems and also affect digestion and reproduction. Cystic fibrosis is the most prevalent fatal genetic disease in the United States, affecting about 30,000 Americans. There is currently no cure for cystic fibrosis, but there are several therapies that may help to alleviate symptoms. CF patients are at a higher risk of developing other health problems, such as liver disease, lung damage, sinusitis, and bacterial infection. CF support groups are available to assist CF patients in learning more about their disease, connecting with doctors, and educating the public
Causes of Cystic Fibrosis
Cystic fibrosis is caused by a mutation in the gene cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator(CFTR). The CFTR gene defect causes the CFTR protein to become dysfunctional. This protein is necessary for chloride transport to the cell surface. Without this protein chloride is unable to move and attract water to the cell surface, making the mucus more sticky and thick. Another most frequent mutation, F508, is a deletion of three nucleotides that results in the loss of phenylalanine (F) amino acid at the 508th position on the protein. There are over 1500 different mutations that can result in cystic fibrosis.
Cystic fibrosis is a recessive genetic disease. This implies that both parents must have the gene in order for their child to be affected. If one parent has CF and the other does not, they have a 1:2 chance of having a kid with the condition.
Cystic fibrosis can be caused by a variety of environmental factors, including cigarette smoke, air pollution, and germs.
Fig: Cystic Fibrosis Airways
Causes of Cystic Fibrosis
Cystic fibrosis is caused by a mutation in the gene cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator(CFTR). The CFTR gene defect causes the CFTR protein to become dysfunctional. This protein is necessary for chloride transport to the cell surface. Without this protein chloride is unable to move and attract water to the cell surface, making the mucus more sticky and thick. Another most frequent mutation, F508, is a deletion of three nucleotides that results in the loss of phenylalanine (F) amino acid at the 508th position on the protein. There are over 1500 different mutations that can result in cystic fibrosis.
Cystic fibrosis is a recessive genetic disease. This implies that both parents must have the gene in order for their child to be affected. If one parent has CF and the other does not, they have a 1:2 chance of having a kid with the condition.
Cystic fibrosis can be caused by a variety of environmental factors, including cigarette smoke, air pollution, and germs.
Symptoms of Cystic Fibrosis
Cystic fibrosis can affect people in different ways, but the most common symptoms are breathing difficulties, digestive issues, chronic sinus infections, and infertility. Wheezing, coughing, and shortness of breath are examples of breathing issues. Digestive issues can cause poor nutrition absorption, weight loss, and diarrhea. Reproductive problems can lead to infertility in men and women. Because mucus builds up in the lungs over time, they become damaged and stop working, thus lung transplant is commonly advised for these individuals.
B. Cepacia and Cystic Fibrosis
Burkholdeia cepacia is a gram negative bacteria found in the natural environment. It is known for exhibiting antibiotic resistance to several drugs. As a result, once it reachs the lungs, treating it becomes very difficult in CF patients. Combination therapy is used to overcome B. cepacia infection.People who have immunodeficiencies or cancer may also acquire B. cepacia. CF patients are more likely than others to get B. cepacia. It may cause the rate of lung function to drop more rapidly and result in a shorter life expectancy. B. cepacia can spread through direct or indirect contact, and so it is advised to wear gloves and masks during social gatherings. Throat or sputum culture is used for B. cepacia diagnosis.
How is Cystic Fibrosis diagnosed?
Cystic fibrosis can be diagnosed with a genetic test. Blood or saliva is tested for a particular gene that is associated with cystic fibrosis. The CFTR gene is a powerful predictor of the disease, as it determines whether or not someone has cystic fibrosis. If the gene is identified, it indicates that the individual has cystic fibrosis and will require therapy. Genetic tests are also used for screening carriers of CF mutated genes Heel prick screening test is carried out for newborn babies to check for rare genetic mutations and cystic fibrosis is also checked in that routine. Sweat test helps in diagnosis of CF by measuring the concentration of salt (amount of chloride) in CF patients body. It is the most reliable screening method for CF.
How is Cystic Fibrosis treated?
There is no cure for cystic fibrosis, but there are treatments available that can help manage the symptoms. Some of the treatments include medications, therapies, and surgery.
- Medications may include antibiotics to fight infection, bronchodilators to open airways, and pancreatic enzymes to help digestion.
- CFTR modulators - CF patients with mutation in cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductor regulator gene (CFTR) have dysfunctional CFTR protein. Hence chloride ions cannot move till the cell surface leading to the formation of thick, sticky mucus that clogs the lungs, pancreas, and sinuses. These CFTR modulators are a class of drugs which target CFTR protein. Even though it does not restore the complete movement of chloride ions still it improves the flow which makes CF patients' condition better.
- Therapies may include chest physical therapy to loosen mucus, airway clearance techniques to remove mucus, and nutritional counseling to ensure a healthy diet. There is no known way to prevent cystic fibrosis, but early diagnosis and treatment can improve the prognosis. Parents who are concerned that their child may have cystic fibrosis can have them tested for the gene. If the child has the gene, they can begin treatment right away and may have a better prognosis.
- The prognosis for cystic fibrosis depends on the severity of the disease and the individual and ability to manage the symptoms.According to the severity of the condition, patients' life expectancies vary. Some individuals with CF may live up to 60 or 70 years old. Early diagnosis and treatment are important for improving the prognosis.
Research on CF and Treatment
There is no cure for cystic fibrosis, but scientists are continuing to develop new therapies. The development of gene therapy, stem cell therapy, and genetic modification in the treatment of CF is still being studied. In 2021, few advancements were made using CRISPR/CAS9 technology researchers corrected mutations that cause cystic fibrosis in cultured human stem cells. To repair the defective portion of DNA, they used prime editing, which entails replacing the faulty snippet with a healthy one. In this example, prime editing is said to be less harmful than CRISPR/Cas9. Currently several clinical trials are carried out for testing new treatment possibilities.
CF Related ELISA Kits
ELISA Kits
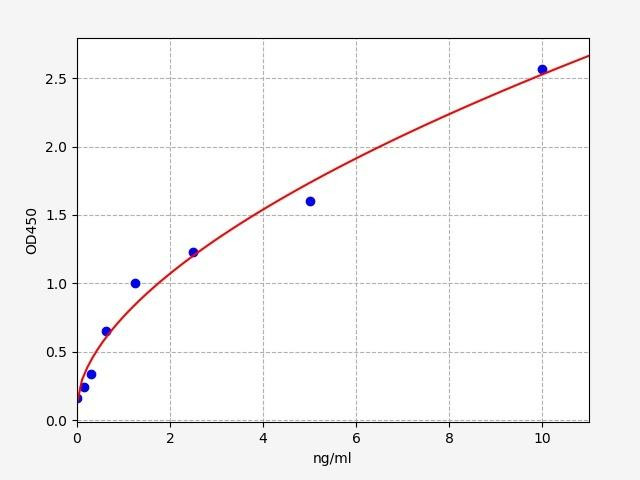
| Human CFTR / Cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator ELISA Kit | |
|---|---|
| Sensitivity | 0.094ng/ml |
| Range | 0.156-10ng/ml |
| ELISA Type | Sandwich |

| Human CFTR (Cystic Fibrosis Transmembrane Conductance Regulator) ELISA Kit | |
|---|---|
| Sensitivity | 0.09ng/mL |
| Range | 0.16-10ng/mL |
| ELISA Type | Sandwich |
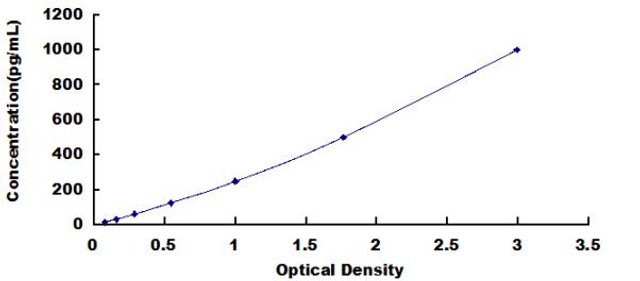
| Human CFTR (Cystic Fibrosis Transmembrane Conductance Regulator) CLIA Kit | |
|---|---|
| Sensitivity | 18.75pg/mL |
| Range | 31.25-2000pg/mL |
| ELISA Type | Sandwich |
Recent Posts
-
Inflammasome Activation Pathways: A Comprehensive Overview
Inflammasomes are complex intracellular structures that play a pivotal role in the immune respon …29th Apr 2024 -
Illuminating the Multifaceted Role of Acetylation: Bridging Chemistry and Biology Introduction:
Acetylation, a chemical process characterized by the addition of an acetyl functional group t …16th Apr 2024 -
Understanding IgA Test: Importance, Procedure, and Interpretation
The IgA test, also known as immunoglobulin A test, is a diagnostic tool used to measure the l …15th Apr 2024