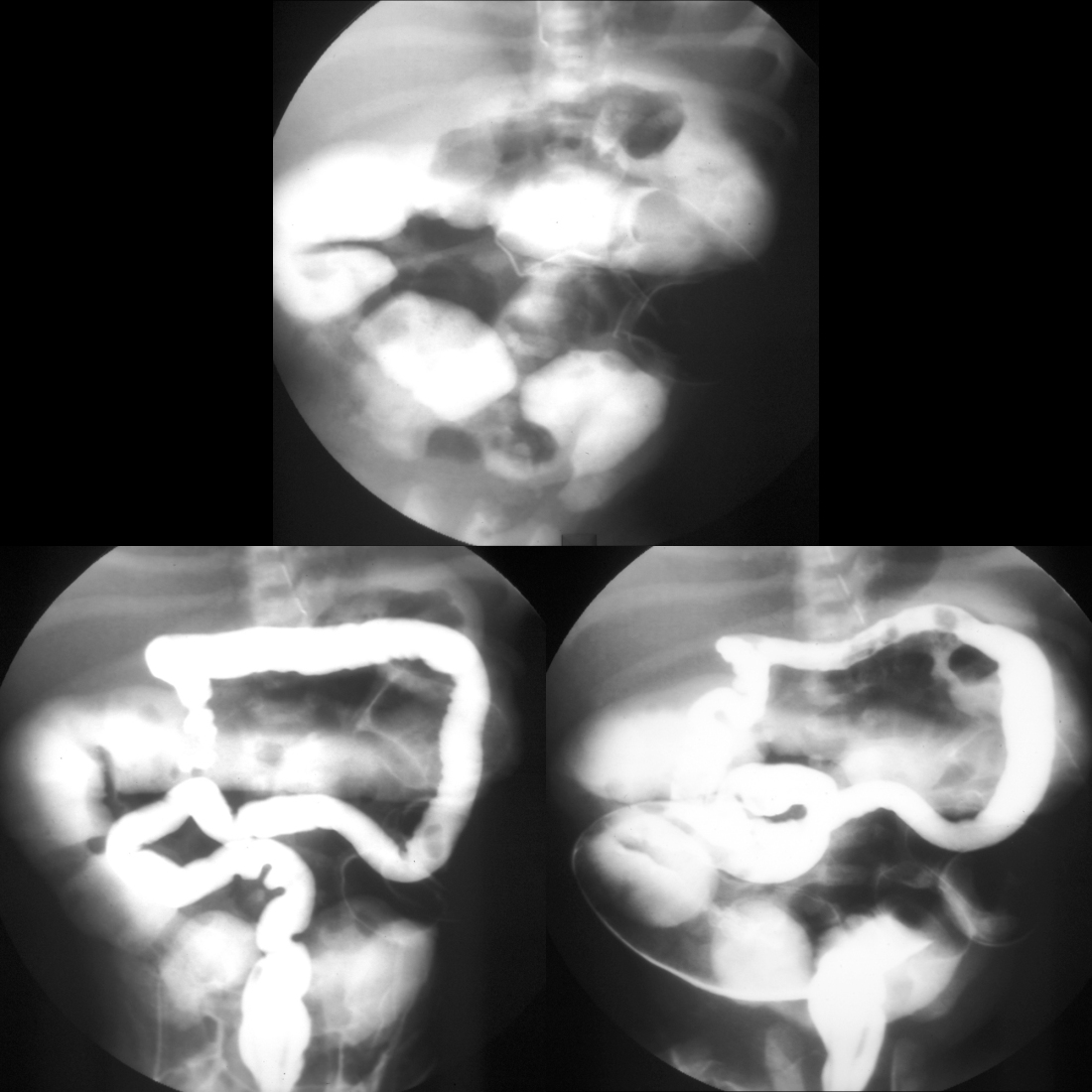
- Etiology: thick meconium causing in-utero distal ileal obstruction
- AXR: bubbly bowel contents in right lower quadrant
- Enema: smallest of all microcolons with multiple small meconium filling defects in colon and terminal ileum and normal caliber terminal ileum with a very dilated distal ileum
- Treatment: high osmolar water soluble contrast enema (diluted 1 part contrast: 2 parts sodium chloride) which must be refluxed above terminal ileum into dilated distal ileum in order to be successful (50% success rate)
- Clinical: most cases are associated with cystic fibrosis, 20% of cystic fibrosis patients develop it
Radiology Cases of Meconium Ileus Uncomplicated