- Etiology: intrinsic airway lumen narrowing due to dysplastic bronchial cartilage or extrinsic airway lumen narrowing leading to congenital ball valve effect and hyperinflated lobe
- CXR: single large lesion with retention of fluid at birth and air trapping later
- Imaging: Usually unilateral and involves one lobe, usually affects upper lobes (left upper lobe > right middle lobe > right upper lobe > lower lobes), has normal blood supply from pulmonary artery
- Clinical: symptomatic during infancy
Radiology Cases of Congenital Lobar Emphysema

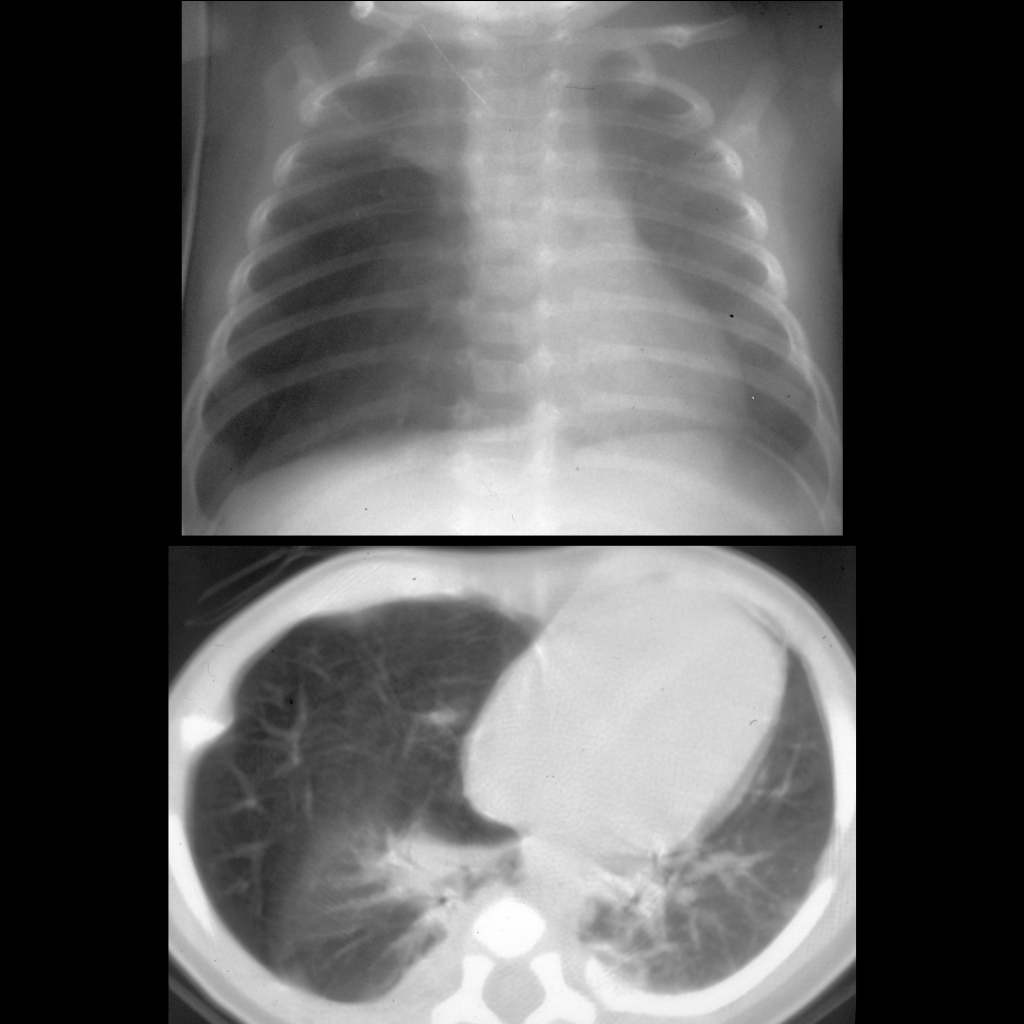
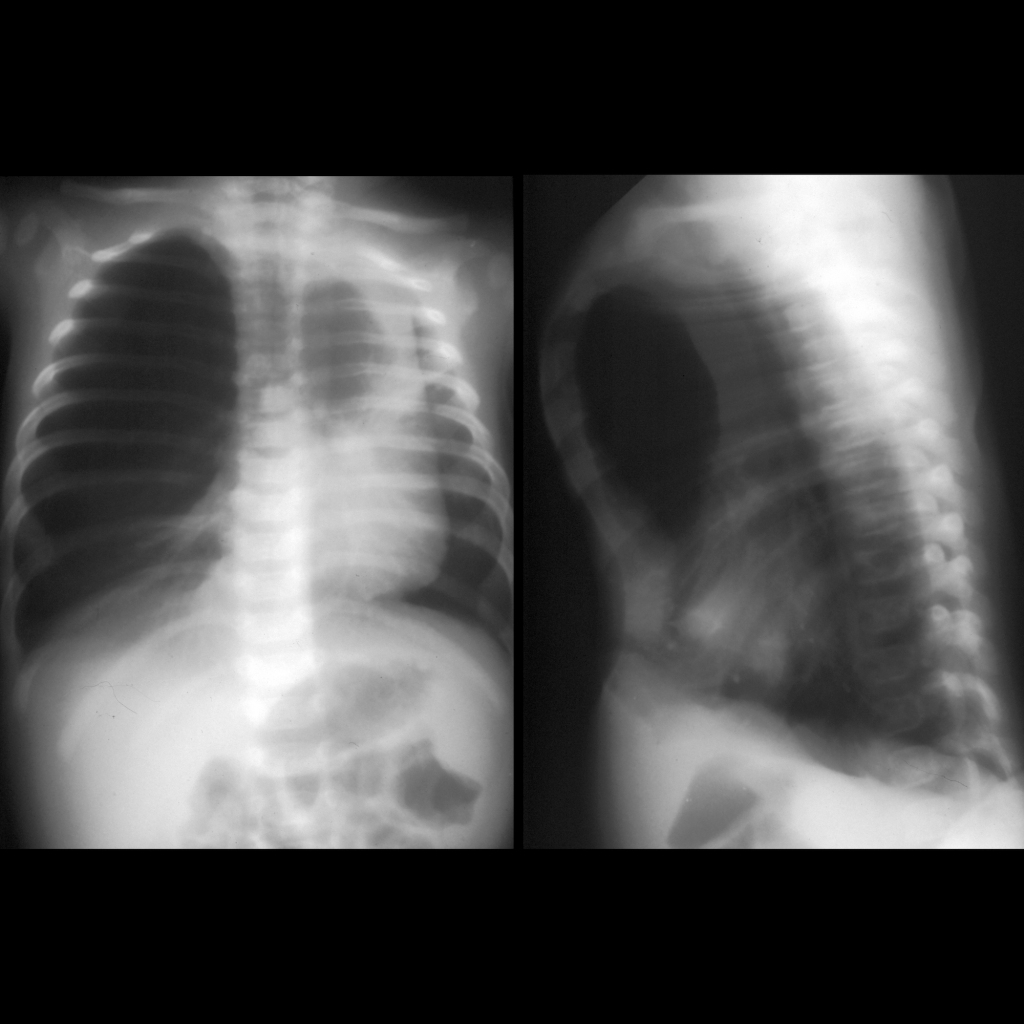
Clinical Cases of Congenital Lobar Emphysema

Surgery Cases of Congenital Lobar Emphysema

Gross Pathology Cases of Congenital Lobar Emphysema

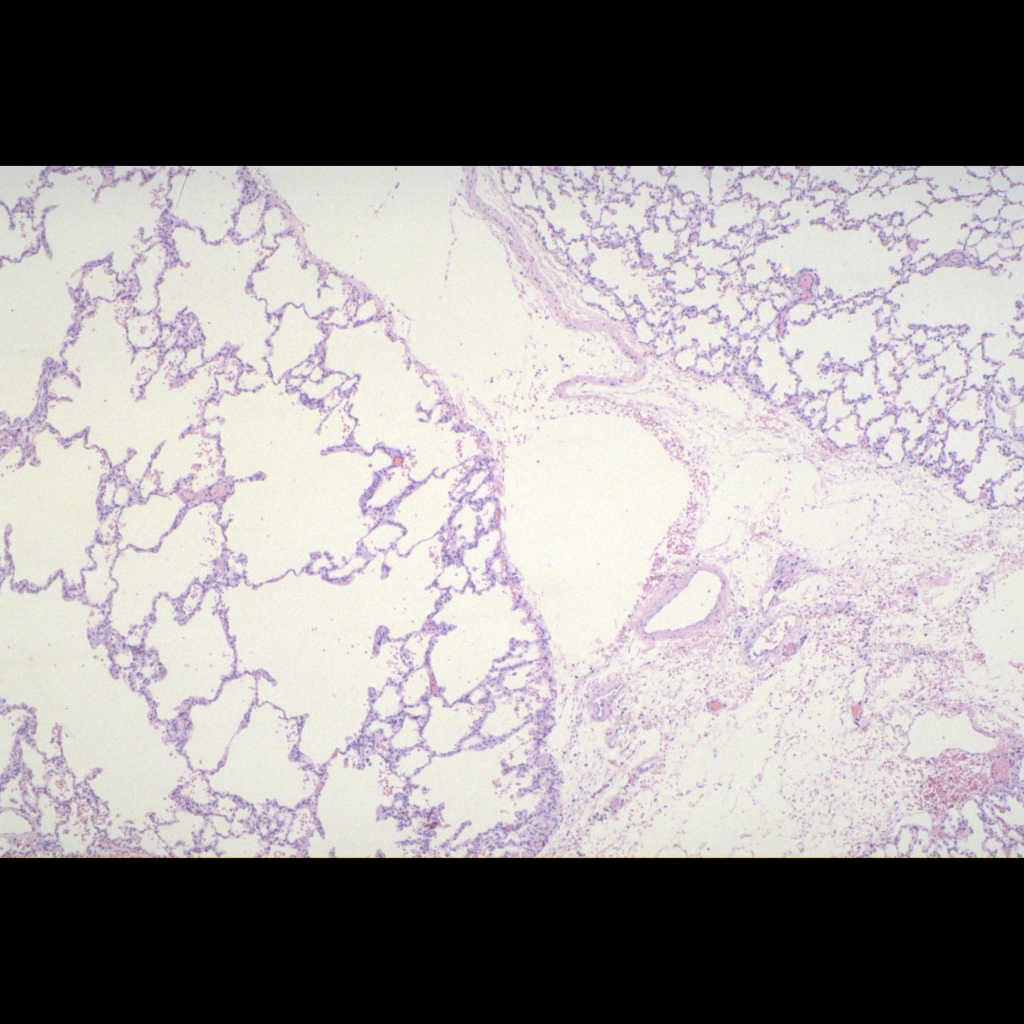
Histopathology Cases of Congenital Lobar Emphysema